CAREC Program
What is CAREC?
The Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation (CAREC) Program is a partnership of 11 countries and development partners working together to promote development through cooperation, leading to accelerated economic growth and poverty reduction. It is guided by the overarching vision of “Good Neighbors, Good Partners, and Good Prospects.”
The program is a proactive facilitator of practical, results-based regional projects, and policy initiatives critical to sustainable economic growth and shared prosperity in the region. Since its inception in 2001 and as of December 2023, CAREC has mobilized $51.02 billion in investments that have helped establish multimodal transportation networks, increased energy trade and security, facilitated free movement of people and freight, and laid the groundwork for economic corridor development.
CAREC 2030 provides the new long-term strategic framework for the program leading to 2030. It is anchored on a broader mission to connect people, policies and projects for shared and sustainable development, serving as the premier economic and social cooperation platform for the region.
KEY DOCUMENT: CAREC 2030: Connecting the Region for Shared and Sustainable Development | РУССКИЙ
Who are the members of CAREC?
What does CAREC do?
As the reintegration of the Eurasian continent gathers speed, the CAREC countries are poised to reap substantial benefits. With the rapid economic expansion of the People’s Republic of China and Japan to the east, the Russian Federation to the north, and India and Pakistan to the south, there is a real and growing demand for improved connections between Europe and Asia. This momentum provides CAREC countries with an unprecedented opportunity to emerge as a center for trade and commerce, to achieve higher levels of economic growth, and to reduce poverty.
None of the region’s economies will be able to fully capture this opportunity in isolation. But all will benefit from working together, and with their neighbors, to build on their strengths for mutual progress.
Turning this potential into reality will require significant improvement in the region’s physical infrastructure such as roads, aviation and rail systems; in the way the region manages its shared resources to support efficient and rational use of energy and water; in progress toward harmonizing and modernizing its customs administrations, and streamlining the rules and procedures that govern countries’ international trade relationships; and in efforts to promote and strengthen people-to-people contacts across borders.
The six CAREC transport corridors are building a truly global future for the region, linking markets in northern People’s Republic of China to Azerbaijan in the Caucasus and further to Europe, and from Kazakhstan to Pakistan’s warm-water ports of Karachi, Gwadar, and beyond.
Seamless connectivity is moving people and their businesses along the CAREC corridors faster, speeding up passage, and reducing the costs of crossing borders.
CAREC corridors improve access to essential services and job opportunities – ultimately ensuring a better quality of life for all people of the CAREC region.
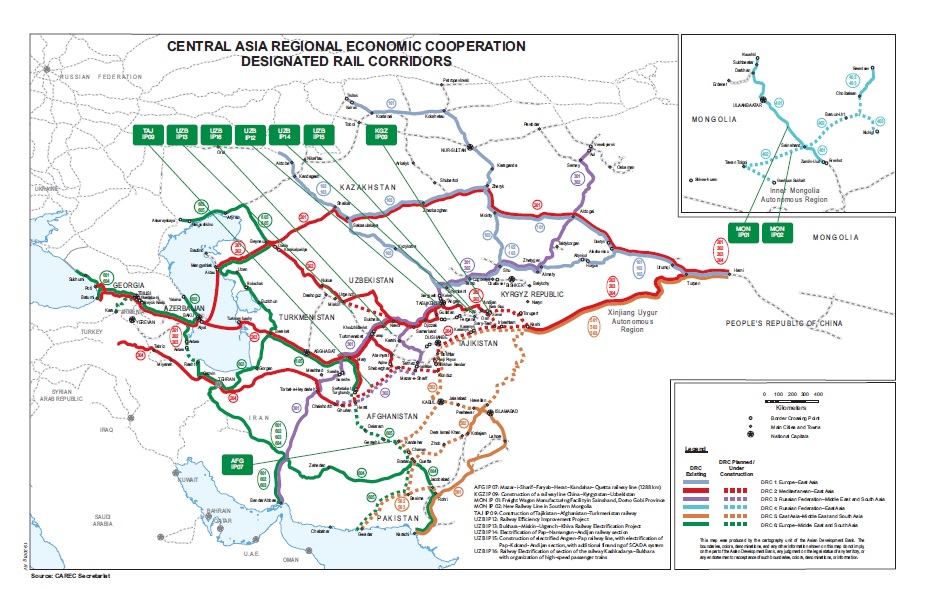
Learn more about CAREC Corridors
CAREC’s development partners facilitate financing for regional projects that benefit the entire CAREC region, and also ensure the quality of investments made by providing strategic and technical advice.
The CAREC Institute plays a key role in providing knowledge solutions and capacity building services in CAREC’s operational priorities to help uplift policy development, and facilitate sharing of experiences and best practices across member countries.
What has CAREC achieved?
Since 2001, the Program has recorded impressive achievements in regional economic cooperation, particularly in the areas of transport, energy, trade, and economic corridors development. From 2001 to 2020, investments in member countries have amounted to $40 billion, covering 213 projects. Latest achievements per sector are listed below.
Transport
- 9,964 kilometers (km) of expressways or national highways built, upgraded or improved as of 2017 (surpassing the TTFS 2020 target of 7,800 km or roads constructed or improved by 2020)
- 1,995 km of new railways built as of 2017 (surpassing the TTFS 2020 target of 1,800 km of new railways built by 2020)
- 3,433 km of railways improved as of 2017 (surpassing the TTFS 2020 target of improving 2,000 km of railways by 2020)
- 1 port (Aktau) completed and 2 border-crossing points (BCPs) improved (Dusti and Guliston); 1 port (Turkmenbashi), 2 logistics centers (Turkmenbashi and Zamyn-Uud) and 4 BCPs (Karamyk, Torkham, Chaman, Wagha) ongoing
- Railway strategy developed to guild the long-term development of railways in the CAREC region
- Road safety strategy developed to make CAREC corridors safer
- Three knowledge products on road safety engineering completed
- Three knowledge products on road asset management completed
- Scoping study to understand the potential role of CAREC in creating an efficient aviation market in the region completed
KEY DOCUMENT: CAREC Transport Strategy 2030
Trade
- Regional technical assistance projects support customs cooperation in five priority areas: (i) simplification and harmonization of customs procedures, which is the core requirement of the Revised Kyoto Convention; (ii) information and communication technology development and data exchange, (iii) risk management and post-entry audit, which includes the periodic conduct of time release studies and the adoption of Authorized Economic Operators programs; (iv) joint customs control; and (v) regional transit development
- Pilot testing of the CAREC Customs Information Common Exchange and the CAREC Advanced Transit System
- Assessment of CAREC member countries’ readiness to implement the World Trade Organization Trade Facilitation Agreement
- Implementation of the CAREC Common Agenda for Modernization of Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures for trade facilitation
- Regional Improvement of Border Services (RIBS), designed to coordinate infrastructure improvements and border crossing clearance procedures in select border crossing points, are being implemented in four countries: the Kyrgyz Republic, Mongolia, Pakistan, and Tajikistan
- 22-member CAREC Federation of Carrier and Forwarder Associations (CFCFA) active throughout the region
KEY DOCUMENT: CAREC Integrated Trade Agenda 2030 and Rolling Strategic Action Plan 2018–2020
Energy
- Inaugural CAREC Energy Investment Forum introduced CAREC as a single significant market to suppliers of clean energy technologies
- Technical assistance aims to further develop technical capacity and understanding government officials and institutions in CAREC member countries, and create an enabling environment for policies and regulations to support clean energy technology adoption
- 1,697 kilometers (km) of transmission lines installed or upgraded in Q1, 2017 (total of 645,428 km, as of 2016)
- Energy generation capacity increased by 5,482 megawatts (mw) in Q1, 2017 (total of 132,156 mw as of 2016)
- 870 new substations installed and 206 substations upgraded in Q1, 2017
KEY DOCUMENT: CAREC Energy Strategy 2030: Common Borders. Common Solutions. Common Energy Future.
Key Publications
CAREC Timeline

1996

1997

1998
2000
2001

2002

2003

2004

2005

2006
The First Business Development Forum sees business leaders and policy makers find ways to reduce impediments to regional cooperation

2007

2008

2009

2010

2011

2012

2013

2014

2015

2016

2017

2018

2019

2020

2021

2022



















