Trade
CAREC will help assess the shifting landscape of global and regional trade, and the potential of moving toward free trade agreements in the region, with a focus on trade in services, including tourism. It will assist members with the range of World Trade Organization (WTO)-related commitments, with respect to trade facilitation and policy. Support for national single windows, improved border crossing points, and customs harmonization will be provided. Economic corridor development and related urbanization strategies will be facilitated.
CAREC Integrated Trade Agenda 2030
The trade strategy is embodied in the CAREC Integrated Trade Agenda (CITA) 2030 to assist CAREC members integrate better into the global economy, ultimately enhancing their growth potential and improving the living standards of people in the region. CITA comprises three pillars.

Related Documents:
Trade, Tourism, and Economic Corridors Cluster Progress Report (July 2023 to June 2024) | RUS | CHN
Trade, Tourism, and Economic Corridors Cluster Progress Report (July 2022 to June 2023) | RUS | CHN
Trade, Tourism, and Economic Corridor Cluster Progress Report (July 2021 – June 2022) | RUS| CHN
Trade Sector Progress Report (June 2020 – July 2021) | RUS
Trade Sector Progress Report (September 2019–September 2020) | RUS
Institutional Structure
CITA’s institutional framework is guided by strong country and development partner ownership, effective engagement with the private sector, and coordination with other stakeholders.
Under the policy and strategic directions of the Ministerial Conference and oversight of the Senior Officials’ Meeting, the Regional Trade Group (RTG) will be the lead coordinative and consultative body for overarching trade issues. The Customs Cooperation Committee (CCC) will continue to be responsible for all customs-related issues. Both the RTG and CCC shall closely coordinate and cooperate with each other, supported by expert groups in technical areas as may be established.
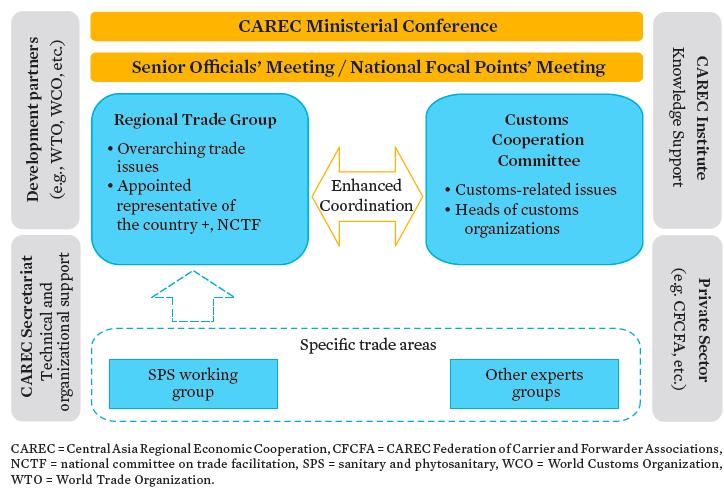
Regional Trade Group
The Regional Trade Group (RTG) is the lead consultative and coordinating body with full operational authority over CAREC work on trade as embodied in CITA 2030 and the accompanying Rolling Strategic Action Plans (RSAP). Policy and strategic direction will be provided by the Ministerial Conference, and oversight by the Senior Officials’ Meeting. Members consist of all Appointed Representatives of the Country (ARCs). The RTG oversees policy dialogue and strategy formulation, project pipeline development, implementation and monitoring, and institutional strengthening and stakeholder coordination.
Customs Cooperation Committee
The Customs Cooperation Committee (CCC) continues to be the responsible body for all customs-related matters. Established in January 2002, the CCC is composed of the heads and deputy heads of customs organizations of the 11 CAREC member countries. The CCC aims to facilitate regional trade through concerted customs reforms and modernization, strengthened inter-agency coordination, and enhanced partnerships with the private sector to eliminate trade barriers to development. The CCC also serves as the regional forum for addressing issues of common interest relevant to trade facilitation, and is expected to provide the leadership in advancing trade facilitation initiatives.
Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures Regional Working Group
The Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (SPS) Regional Working Group (RWG) is the policy-making body for the implementation of the Common Agenda for the Modernization of SPS Measures for Trade (CAST), which was adopted during the 2015 CAREC Ministerial Conference. The RWG develops the annual SPS work program based on national plans and the RSAP, and coordinates progress and planned activities with the RTG.
Key Projects
As of December 2023, nearly $1.4 billion (2.7% of the total CAREC Project Investments) has been invested among the member countries. Five trade-related projects valued at $759 million were approved between 2018-2023. Most recent projects approved include the Border Efficiency for Sustainable Trade project and Developing Economic Cooperation Zone project (both in Mongolia), and the Inner Mongolia Sustainable Cross-Border Development Investment Program for the PRC. The Regional Improvement of Border Services (RIBS) projects in Kyrgyz Republic, Mongolia, Tajikistan, and Pakistan supported these countries in upgrading their border infrastructure, facilities and systems, and established national single window (NSW) system for some. The NSW increased visibility of trade operations resulting to improved compliance and customs revenue collection. Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Uzbekistan are accelerating the testing phase of the prototype for CAREC Advanced Transit System (CATS) and Information Common Exchange initiative since signing the CATS Memorandum of Understanding in October 2023.
Beyond physical infrastructure development, substantial progress has been achieved in the soft component, i.e., improving capacities and supporting reforms to align with international standards and best practices. A key aspect is the support to World Trade Organization (WTO) accession of three remaining CAREC members (Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan). CAREC remained committed to implementing the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) and has acceded to key international agreements crucial for trade. CAREC members also started leveraging global solutions to facilitate trade and digitizing trade processes. Uzbekistan and Pakistan have successfully integrated into the global ePhyto solutions and are exchanging electronic sanitary and phytosanitary certificates, with other members in the onboarding process. Countries are also piloting emerging technologies with support from the CAREC Program, such as robotic process automation or artificial intelligence (AI) for Georgia’s trade procedures and blockchain or digital ledger technology for Mongolia’s electronic certificates of origin, with potential to scale up or be replicated in other CAREC countries.
In addition, the sector developed and maintains the CAREC Corridor Performance Measurement and Monitoring (CPMM). It is an empirical tool designed to assess the efficiency of the CAREC six priority transport corridors using actual time and cost data collected by private sector transport associations.
For additional information, please follow the links provided above.



