Health
The CAREC 2030 strategy supports health sector cooperation to face pandemic risks, control communicable diseases, and address non-communicable diseases. Since the strategy’s endorsement in 2017, this agenda has progressed, starting with a scoping study on CAREC health cooperation, the formation of the CAREC Working Group on Health, and the approval of the CAREC Health Strategy 2030.
Health at the Crossroads of Regional Interconnectedness
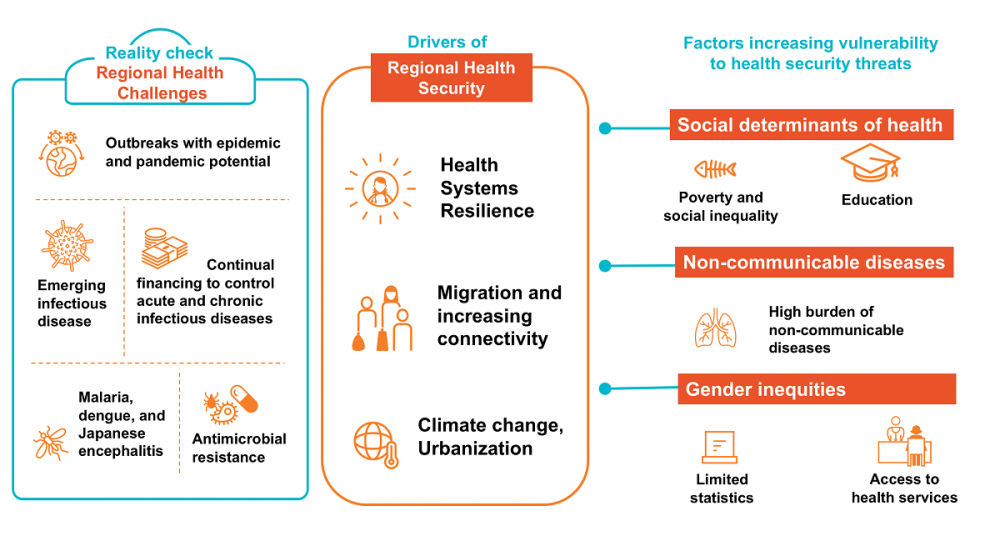
The CAREC region is becoming increasingly interconnected, with a growing mobile population and rapidly developing urban hubs. These factors, together with the importance of livestock production to the region’s economy, make it especially prone to communicable disease outbreaks and epidemics.
Most recently the COVID-19 pandemic has starkly illustrated the persistent threat from emerging infectious diseases of animal origin, with pandemic potential that can move across continents within a few months.
Some CAREC countries are also exposed to outbreaks of other communicable diseases, including malaria, dengue, and Japanese encephalitis, that may spread regionally. Chronic infectious diseases such as viral hepatitis B and C, HIV and tuberculosis are also a heavy burden in the region. At the same time, the extent of antimicrobial resistance to inexpensive and effective antimicrobial drugs is alarming, making many common diseases difficult and expensive to treat.
Health Security Under Threat
The resilience of health systems is one the main drivers of health security, which is undermined by gaps in health systems funding, human resources, laboratory capacity and disease surveillance. Climate change and growing urbanization exacerbate health security risks such as antimicrobial resistance and natural disasters. Migration is also a key driver, adversely affecting people’s living conditions and access to health care services. Gender inequities, social determinants of health as well as the high burden of noncommunicable diseases in the region increase the population’s vulnerability to health security threats.
Because public health threats such as infectious diseases outbreaks can quickly cross borders and become a cross-border concern, they can only be effectively addressed through regional cooperation on health security. CAREC countries need to work together to manage health risks, and also to collaborate on health systems strengthening and the health of migrants, mobile populations and border communities. Only then can they mitigate the impact of health security threats on human lives, health systems, and the economy.
Scoping Study on CAREC Health Cooperation
In 2019, ADB commissioned a scoping study to explore the potential and opportunities for promoting regional cooperation in the health sector. The study recommended establishing a regional health coordination mechanism and developing a regional health strategy and investment framework. The CAREC Working Group on Health was established in March 2021 to guide CAREC health cooperation and the development of a CAREC health strategy towards 2030.
CAREC Health Strategy 2030
The CAREC Health Strategy 2030 supports health cooperation. It has a particular focus on enhancing health security through regional cooperation. This strategy will benefit the population of every CAREC country, including migrants and the vulnerable population groups.
The CAREC Health Strategy 2030 emerged from extensive consultations with countries and development partners, starting in October 2020 with the first CAREC Country Consultation on Health Sector. In March 2021, at a Virtual Regional Inception Workshop, experts from CAREC countries and other stakeholders began the process of formulating the strategy, followed by country cluster consultations in July 2021. The Working Group on Health gathered again in September 2021 for a Virtual Consultation Meeting to finalize the strategy, ahead of its endorsement on November 17 2021 at the 20th CAREC Ministerial Conference.
Vision: Public health threats in the CAREC region are addressed comprehensively, efficiently and sustainably, through adopting a regional approach, while safeguarding the needs of the most vulnerable segments of the population.
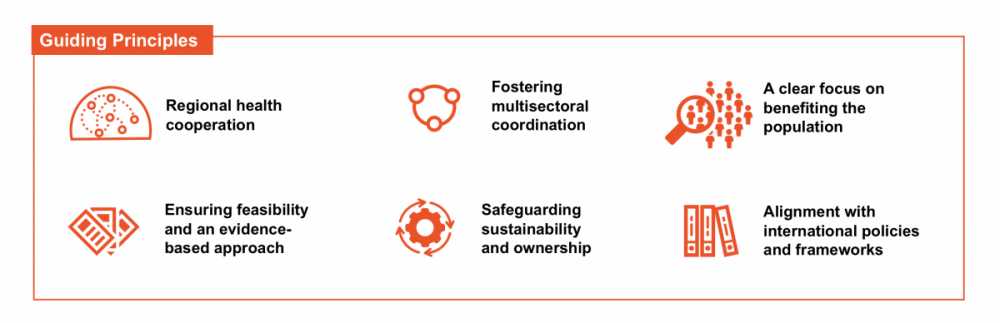
Guiding Principles
- Cooperation between countries
- Multisectoral coordination
- Evidence-based approach
- Safeguarding sustainability and ownership
- Alignment with international policies and frameworks.
Strategic Pillars
The CAREC Health Strategy 2030 builds on four main pillars
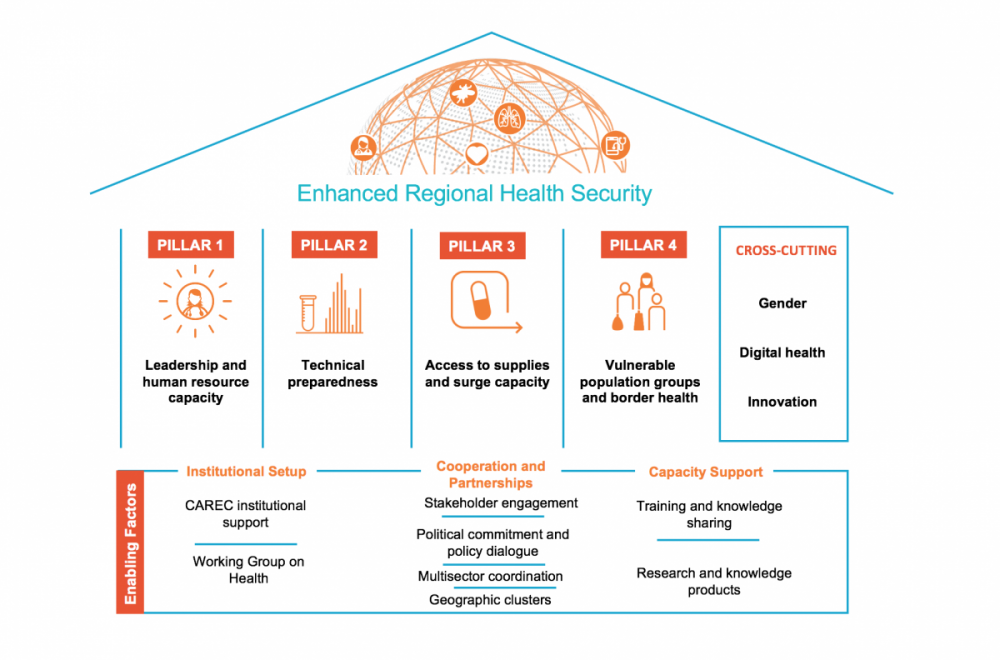
Pillar 1: Leadership and Human Resource Capacity
Improved policy coordination within and between countries enables every country to better respond to epidemic and pandemic health threats. Human resource capacity must address the aging workforce, recruitment of the right mix of staff, the current maldistribution of health care workers between rural and urban areas, education and harmonization of standards, and capacity development for policymakers, health managers, and the health workforce to prepare for and respond to health threats and emergencies.
Pillar 2: Technical Preparedness (Laboratories and Surveillance)
Examples include improving surveillance systems, exploring regional dashboards with automated early warning systems, and establishing regionally aligned information materials for awareness on communicable diseases.
Pillar 3: Access to Supplies and Surge Capacity
Increasing supply capacity needs harmonized regulatory mechanisms and standards for medications and supplies, efficient procurement mechanisms, and reliable supply chain management.
Pillar 4: Vulnerable Population Groups and Border Health
To reduce the burden of communicable diseases among migrants, border communities, and vulnerable population groups, they need better access to health services. This entails improving the portability of health care benefits across borders, and joint strategies to improve access to health services for vulnerable populations in border areas. Investment in border health facilities and infection prevention and control are also required.
All four pillars need to be supported by digital health and innovations to support health information systems, data management, and regional knowledge sharing. In addition, data collection disaggregated by gender is key to meeting the specific health needs of women.
Enabling Factors
Implementation has to be enabled by necessary institutional setup, in this case the CAREC-supported Working Group on Health. Partnerships and cooperation with stakeholders such as development partners is another key enabler, with political commitment and policy dialogue on health cooperation among countries, and multisector coordination. In addition, there must be capacity support through training, research and knowledge sharing.
Implementation of the CAREC Health Strategy 2030
The CAREC Working Group on Health is leading the implementation of the CAREC Health Strategy 2030 with support from development partners. This group is composed of high-level representatives from the
health-related government agencies who were appointed by each CAREC country, complemented by multidisciplinary expertise in various sectors on an as-needed basis.
CAREC Health Regional Investment Framework
In addition to the CAREC Health Strategy 2030, a regional investment framework on health was developed to layout a pipeline of regional projects and initiatives under the four strategic pillars to be implemented during the first 5 years of the strategy implementation period (2022-2027).
The framework was developed to help guide partner investments and meet the gap in effectively addressing key regional needs, including protecting vulnerable populations in border areas.
ADB is supporting the CAREC Health work including the strategy’s development with a technical assistance project.
